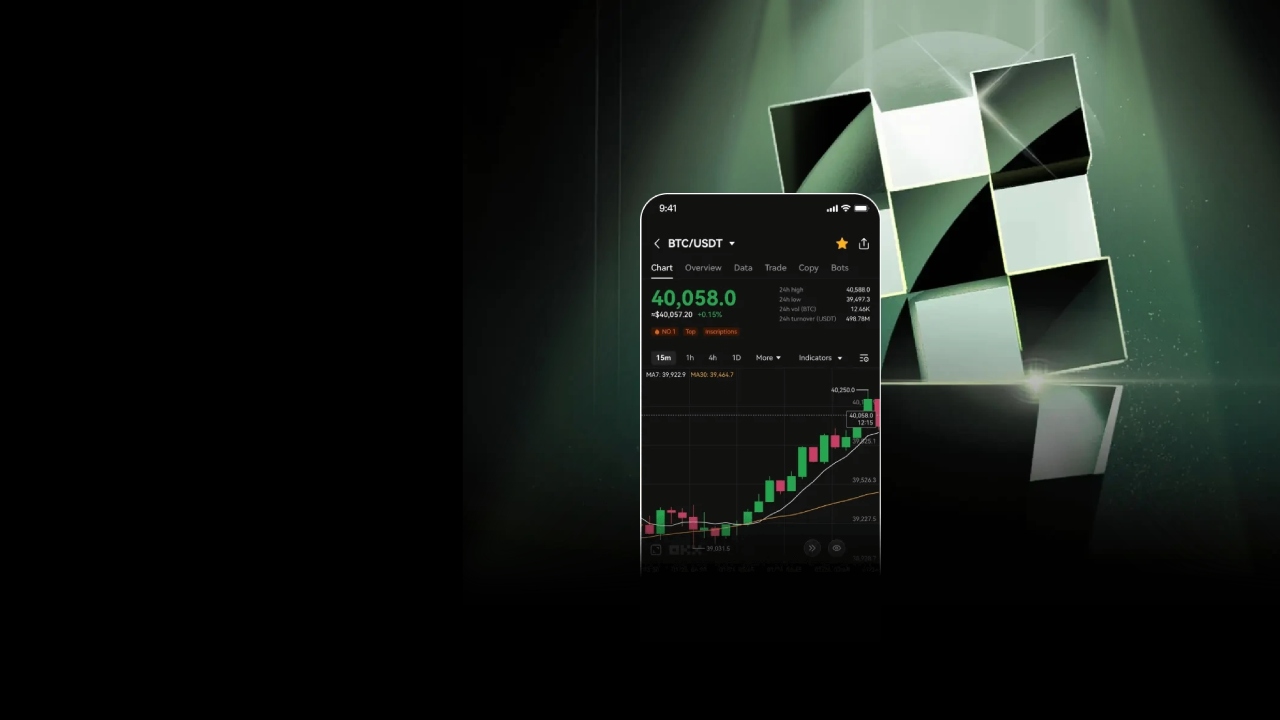
欧易
数字资产交易平台
主要面向全球用户提供比特币、莱特币、以太币等数字资产的币币和衍生品交易服务
保护区块安全
您的第一道安全防线
深受 5,000 万交易员信任,为超 29 万亿美元交易提供保障。欧易 Protect 为您构筑数字资产堡垒,确保资产安全无虞,让您高枕无忧。

5千万 交易员的选择

10年 零事故

29万亿 美元交易量

24小时 客服支持
由业内头部安全专家独立认证
保障每一笔交易、每一个钱包的安全

实时防护
全天候即时威胁监测

交易所
高级系统为每笔交易保驾护航

钱包
多层安全防线,让用户自行控制私钥
欧易可助力您
欧易都提供哪些产品
交易
我们为全球 180 多个地区的数百万用户提供数字货币交易服务。支持超过 700 个法币和数字货币交易对的现货、合约、期权等衍生品交易。
金融
赚取每日奖励,支持 USDT、USDC 及 ETH 等超过 100+ 种不同代币。高安全性交易平台,让您的数字资产安全无虞,收益更加可观。
WEB3 钱包
通过连接 Web3 钱包,管理您的 DeFi 投资组合,通过连接 Web3 钱包,您可以轻松管理全部去中心化资产。管理您的 DeFi 投资组合。
只需几步即可轻松购买数字货币

注册账号
访问欧易网站,并注册属于您的欧易账号

验证身份
登录后上传有效证件,进行个人实名认证

买入数字货币
首页-买币页面一键买币,支付后等待放币
什么是数字货币?
数字货币是采用密码学原理来确保交易安全及控制交易单位创造的交易媒介,也被称为数字货币或虚拟币。与美元或其他法定货币不同,数字货币并不以实物的形式存在,是通过具有构建去中心化账本功能的区块链技术衍生的带有去中心化特点的数字资产。
每一笔数字货币的交易都会被如实记录在区块链中,一旦确认交易及通过验证,即为不可逆。这也就意味着数字货币交易不可逆转、不可篡改。
目前,全球金融机构及互联网企业对数字货币的投资正在大幅增长,证明了数字货币的潜力和未来。同时,投资数字货币不仅是进入具有未来主导地位的去中心化金融领域的最有效途径,同时也是对正在广泛普及的区块链等前沿技术的参与。



常见问题
欧易都提供哪些产品?
欧易是一家致力于创新的数字货币交易所。我们为全球 180 多个地区的数百万用户提供前沿的数字货币交易服务。
欧易可助力您:
交易数百种数字货币和交易对。
通过连接 Web3 钱包,管理您的 DeFi 投资组合,通过连接 Web3 钱包,您可以轻松管理全部去中心化资产。管理您的 DeFi 投资组合。
在欧易的 NFT 市场上创建和交易 NFT。
探索绝佳的去中心化应用,包括 DeFi 和区块链游戏 DApps。
借助欧易 App 或浏览器插件无缝连接到 DeFi。
连接世界知名的 TradingView 平台,利用他们的超强图表来直接进行虚拟货币交易。
如何通过欧易平台购买比特币?
如何通过欧易平台购买比特币?用户可使用英镑、欧元、美元或当地货币轻松快捷地购买比特币。欧易支持各种常用的支付方式,包括 Visa、Mastercard 和 ApplePay 信用卡。 想要快速入门,请查看欧易的最新指南,了解如何在欧易平台上购买比特币。想买卖或持有数字货币生态系统中行情喜人的其他币种吗?探索比特币 (BTC)、以太坊 (ETH) 等数字货币的价格和其他信息,今天就踏上你的数字货币之旅!
什么是活期简单赚币?
简单赚币是欧易打造的一款帮助有闲置数字资产用户进行低门槛赚币的产品,入门简单,并提供活期和定期两种选择。
$37+万亿
平台总交易额
$250+亿
平台资产
$1060+亿
单日交易峰值
5000万+
全球用户总数
从数字货币交易初体验到第一次购买 NFT,欧易将助您轻松赚币
您数字货币之旅的得力助手
官方中文社交媒体
欧易新闻社区
-
SOL 质押完整指南:从机制、收益等方面解析 Solana 质押生态
SOL 质押完整指南:从机制、收益等方面解析 Solana 质押生态 撰文:Lostin,Helius 编译: […]
-
金色Web3.0日报 | 贝莱德比特币现货ETF规模已超越其黄金ETF
金色Web3.0日报 | 贝莱德比特币现货ETF规模已超越其黄金ETF DeFi数据 1.DeFi代币总市值: […]
-
稳定币赛场新动向:下半年23个项目官宣投融资 币安与Circle“世纪大和解”
稳定币赛场新动向:下半年23个项目官宣投融资 币安与Circle“世纪大和解” 作者:Nancy,PANews […]
-
稳定币赛场新动向:下半年23个项目官宣投融资,币安与Circle「世纪大和解」
稳定币赛场新动向:下半年23个项目官宣投融资,币安与Circle「世纪大和解」 原文作者:Nancy,PANe […]
-
美国资本币领涨 盘点与贝莱德等传统资管关联的 18 个发币项目
美国资本币领涨 盘点与贝莱德等传统资管关联的 18 个发币项目 作者:flowie,ChainCatcher […]
-
晚间必读5篇 | 量子芯片Willow为何轰动全球科技界?
晚间必读5篇 | 量子芯片Willow为何轰动全球科技界? 1.2024稳定币新叙事:明确的监管 传统金融的入 […]
-
ai16z、ELIZA和智能体集市:ELIZA真正令人兴奋的地方
ai16z、ELIZA和智能体集市:ELIZA真正令人兴奋的地方 作者:Teng Yan,ChainofTho […]
-
盘点Farcaster的AI Agent代币发射器:会有下一个Clanker吗?
盘点Farcaster的AI Agent代币发射器:会有下一个Clanker吗? 原文标题:Farcaster […]
-
贝莱德概念领涨,盘点与传统资管巨头关联的18个项目
贝莱德概念领涨,盘点与传统资管巨头关联的18个项目 原文作者:flowie,ChainCatcher 原文编辑 […]
-
LBank Labs 2024 Meme赛道研究:破圈与新生 从争议性叙事迈向千亿赛道
LBank Labs 2024 Meme赛道研究:破圈与新生 从争议性叙事迈向千亿赛道 引言 随着加密市场的逐 […]
欧易跨链桥聚合器为你在所有主流跨链桥之间获取最优价格,满足你的一切跨链需求
超过 60 条网络,触达无限新用户





